 |
Analysis of Data from Designed Experiments |
 |
|
Augmented Design |
Analysis Using SPSS
To
test the equality of check variety effects, accession
effects and to compare accessions with check varieties,
treatment contrast analysis is to be performed therefore,
for ease of understanding, recode the accession number and
check variety as follows:
|
C1 |
1 |
|
N3 |
7 |
|
C2 |
2 |
N4 |
8 |
|
|
C3 |
3 |
N5 |
9 |
|
|
C4 |
4 |
N6 |
10 |
|
|
N1 |
5 |
N7 |
11 |
|
|
N2 |
6 |
N8 |
12 |
Main Procedure is:
Start
→All Programs → SPSS for Windows → SPSS 15.0/
SPSS13.0/ SPSS10.0 (based on the version available on your
machine) → Enter data in Data Editor →
Analyze → GLM → Univariate →
yld → [puts yld under
Dependent list: ] → trt →
[puts trt under Fixed Factor(s): ] → blk→
[puts blk under Fixed Factor(s): ] Continue
→ Model... [Opens Model dialogue box] →
Custom → Build Term(s) → Main
effects → [puts trt and
blk under Model:] → Continue →
Paste → in
the syntax editor mode enter the contrast → Run All.
For performing analysis, input
the data in the following format.
{Here
block is termed as blk, treatment as trt and yield as yld.
It may, however, be noted that one can retain the same name
or can code in any other fashion}.
Following
are the brief description of the steps along with screen
shots.
·
Open
Data editor: Start → All Programs →
SPSS for Windows → SPSS 15.0/ SPSS13.0/
SPSS10.0
·
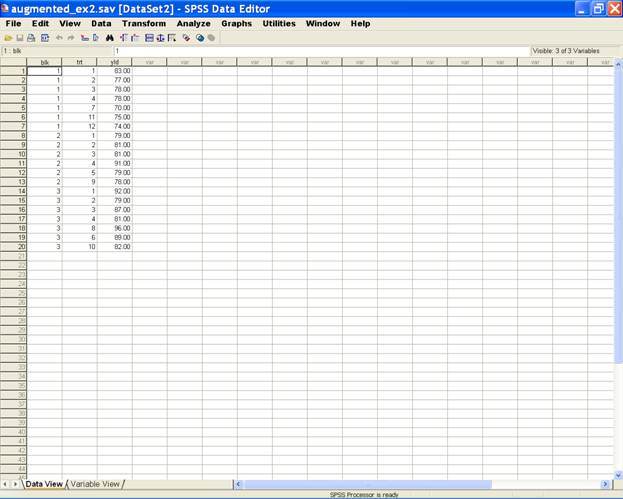
Enter
data in SPSS Data Editor. There are two views in SPSS Data
Editor. In variable view, one can define the name of
variables and variable types string or numeric and data view
gives the spreadsheet in which data pertaining to variables
may be entered in respective columns. In the present case,
we enter data in numeric format.
·
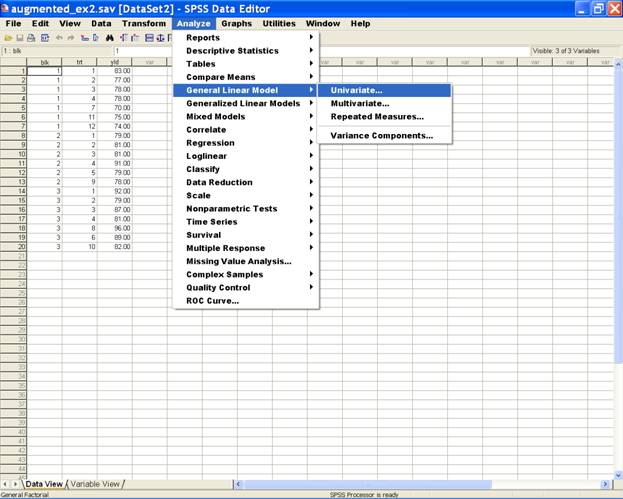
Once
the data entry is complete, Choose Analyze from the Menu
Bar. Now select Analyze
→ General linear Model → Univariate.
·
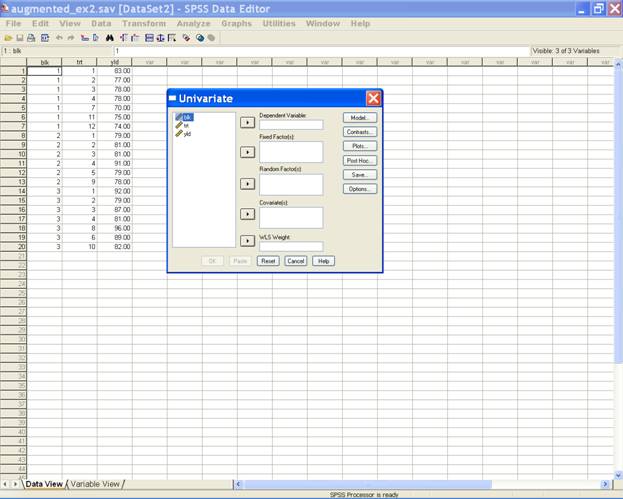
This
selection displays the following screen.
·
Select yld and send
it to the Dependent Variable box; trt and blk may be
selected for Fixed Factor(s) box. After doing these the
dialog box should be like this
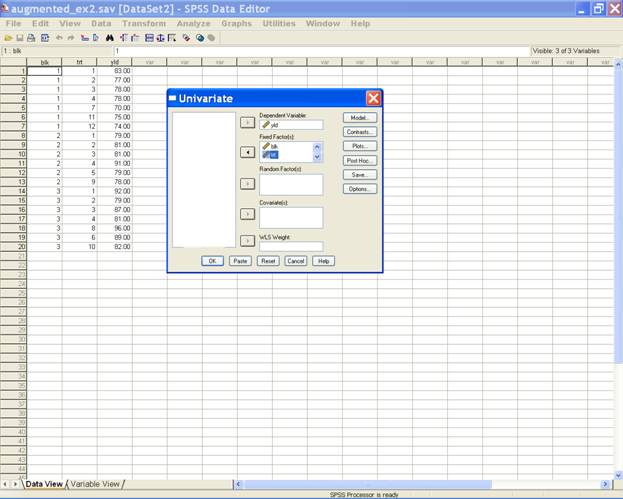
-
Select Model in the Univariate dialog box i.e. → Model... [Opens Model dialogue box] → Custom → Main effects → trt → blk → [puts trt and blk under Model:]. This selection displays the following screen.
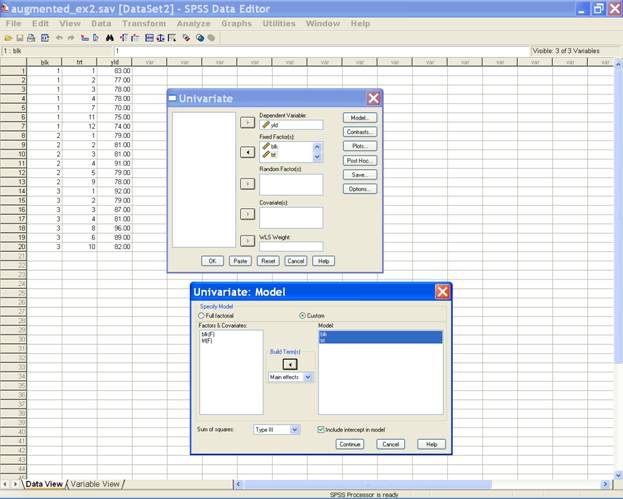
·
Click Continue
to return to the Univariate dialog box.
·
All
possible pair wise treatment comparisons can be performed
using the Button Options on the dialogue box. A click
on Button Options, gives the option for estimated marginal
means and display means for. From the left hand box, take
the effect treatment in the Display means for. Then
check the box Compare main effects and then there are 3
options for confidence interval adjustment viz.
LSD(none), Bonferrnoni and Sidak. Any one of these 3 options
can be selected. Default option is LSD(None).
A screen shot for these options is
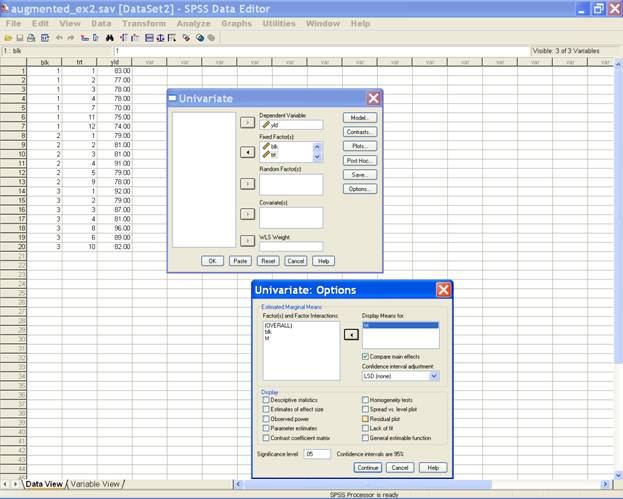
·
Click Continue
to return to the Univariate dialog box.
Since,
here we want to test
i)
the
equality of check variety effects, accession effects.
ii) compare accessions with check varieties.
This
can be done using the contrast analysis.
To perform the contrast analysis one can use the following steps.
·
Click Paste in the Univariate dialog box to get the syntax editor. In the
syntax editor mode define the contrast as:
/LMATRIX
'controls' trt 1 -1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
trt 1 1 -2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
trt 1 1 1 -3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0;
/LMATRIX
'tests' trt 0 0 0 0 1 -1 0 0 0 0 0 0;
trt 0 0 0 0 1 1 -2 0 0 0 0 0;
trt 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 -3 0 0 0 0;
trt 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 -4 0 0 0;
trt 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 -5 0 0;
trt 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 -6 0;
trt 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 -7;
/LMATRIX 'test
vs controls' trt -2 -2 -2 -2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1;
· This selectin displays the following screen
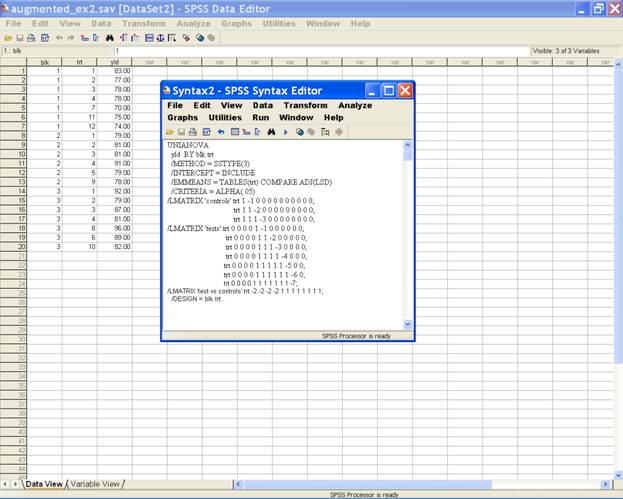
·
Click
Run → All.
-
To answer all the questions 1 to 4, the following syntax may be used after creating the data file.
UNIANOVA
yld BY
blk trt
/METHOD = SSTYPE(3)
/INTERCEPT = INCLUDE
/EMMEANS = TABLES(trt) COMPARE ADJ(LSD)
/CRITERIA = ALPHA(.05)
/LMATRIX
'controls' trt 1
-1 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0
0 0;
trt
1 1 -2
0 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0;
trt 1 1 1 -3
0 0 0
0 0 0
0 0;
/LMATRIX
'tests' trt 0
0 0 0
1 -1 0
0 0 0
0 0;
trt
0 0 0
0 1 1
-2 0 0
0 0 0;
trt 0 0 0
0 1 1
1 -3 0
0 0 0;
trt 0 0 0
0 1 1
1 1 -4
0 0 0;
trt 0 0 0
0 1 1
1 1 1
-5 0 0;
trt 0 0 0
0 1 1
1 1 1
1 -6 0;
trt 0
0 0 0 1
1 1 1
1 1 1
-7;
/LMATRIX 'test
vs controls' trt -2
-2 -2 -2
1 1 1
1 1 1
1 1;
/DESIGN = blk trt .
Analysis Using SAS Analysis Using SPSS Analysis Using SPAD
Home Descriptive Statistics Tests of Significance Correlation and Regression Completely Randomised Design RCB Design
Incomplete Block Design Resolvable Block Design Augmented Design Latin Square Design Factorial RCB Design
Partially Confounded Design Factorial Experiment with Extra Treatments Split Plot Design Strip Plot Design
Response Surface Design Cross Over Design Analysis of Covariance Diagnostics and Remedial Measures
Principal Component Analysis Cluster Analysis Groups of Experiments Non-Linear Models
Copyright Disclaimer How to Quote this page Report Error Comments/suggestions
(Under Development)
For
exposure on SAS, SPSS,
MINITAB, SYSTAT and
MS-EXCEL
for analysis of
data from designed experiments:
Please see Module I of Electronic Book II: Advances in Data Analytical Techniques
available at Design Resource Server (www.iasri.res.in/design)